定义
Cow是一个提供了写时克隆功能的智能指针,它可以包装对数据的借用,当需要修改数据或者获取数据的所有权时,对数据clone。它的定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
pub enum Cow<'a, B>
where
B: 'a + ToOwned + ?Sized,
{
Borrowed(&'a B),
Owned(<B as ToOwned>::Owned),
}
|
Cow名为clone-on-write,但是对数据类型B的trait要求是ToOwned,而不是Clone。这是因为Clone只能从&T生成T,但是ToOwned泛化为从任意给定类型的借用数据构建新类型的数据。功能更为强大。
如下一段示例代码,将Cow应用在结构体中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
use std::borrow::Cow;
struct Items<'a, X: 'a>
where
[X]: ToOwned<Owned = Vec<X>>,
{
values: Cow<'a, [X]>,
}
impl<'a, X: Clone + 'a> Items<'a, X>
where
[X]: ToOwned<Owned = Vec<X>>,
{
fn new(v: Cow<'a, [X]>) -> Self {
Items { values: v }
}
}
// Creates a container from borrowed values of a slice
fn main() {
let readonly = [1, 2];
let borrowed = Items::new((&readonly[..]).into());
match borrowed {
Items {
values: Cow::Borrowed(b),
} => println!("borrowed {:?}", b),
_ => panic!("expect borrowed value"),
}
let mut clone_on_write = borrowed;
// Mutates the data from slice into owned vec and pushes a new value on top
clone_on_write.values.to_mut().push(3);
println!("clone_on_write = {:?}", clone_on_write.values);
// The data was mutated. Let check it out.
match clone_on_write {
Items {
values: Cow::Owned(_),
} => println!("clone_on_write contains owned data"),
_ => panic!("expect owned data"),
}
}
|
运行生成如下结果,可见对借用的数据进行修改后,发生了克隆。
1
2
3
|
borrowed [1, 2]
clone_on_write = [1, 2, 3]
clone_on_write contains owned data
|
使用
试想这样一个场景,我们需要给处理一些Url,其中一部分是https://开头的,而另一部分不是,现在要给缺少https://前缀的Url加上前缀。
使用Cow,函数如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
fn add_prefix_by_cow<'a, T>(urls: T, prefix: &str) -> Vec<Cow<'a, String>>
where
T: IntoIterator<Item = &'a String>,
{
urls.into_iter()
.map(|url| {
if url.starts_with(prefix) {
Cow::Borrowed(url)
} else {
Cow::Owned(String::with_capacity(url.len() + prefix.len()) + prefix + url)
}
})
.collect()
}
|
不使用Cow,函数如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
fn add_prefix_by_clone<'a, T>(urls: T, prefix: &'a str) -> Vec<String>
where
T: IntoIterator<Item = &'a String>,
{
urls.into_iter()
.map(|url| {
if url.starts_with(prefix) {
url.clone()
} else {
url.clone() + prefix
}
})
.collect()
}
|
用Criterion来进行 benchmark 测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
fn bench(c: &mut Criterion) {
let mut group = c.benchmark_group("cow_bench");
group.sampling_mode(SamplingMode::Linear);
group.bench_function("cow", |b| {
b.iter_batched(
|| {
let pre = vec!["https://127.0.0.1".to_string(); 1024];
let non_pre = vec!["127.0.0.1".to_string(); 1024];
[pre, non_pre].concat()
},
|v| {
let _ = add_prefix_by_cow(&v, "https://");
},
BatchSize::SmallInput,
)
});
group.bench_function("clone", |b| {
b.iter_batched(
|| {
let pre = vec!["https://127.0.0.1".to_string(); 1024];
let non_pre = vec!["127.0.0.1".to_string(); 1024];
[pre, non_pre].concat()
},
|v| {
let _ = add_prefix_by_clone(&v, "https://");
},
BatchSize::SmallInput,
)
});
group.finish();
}
|
输出如下:
1
2
|
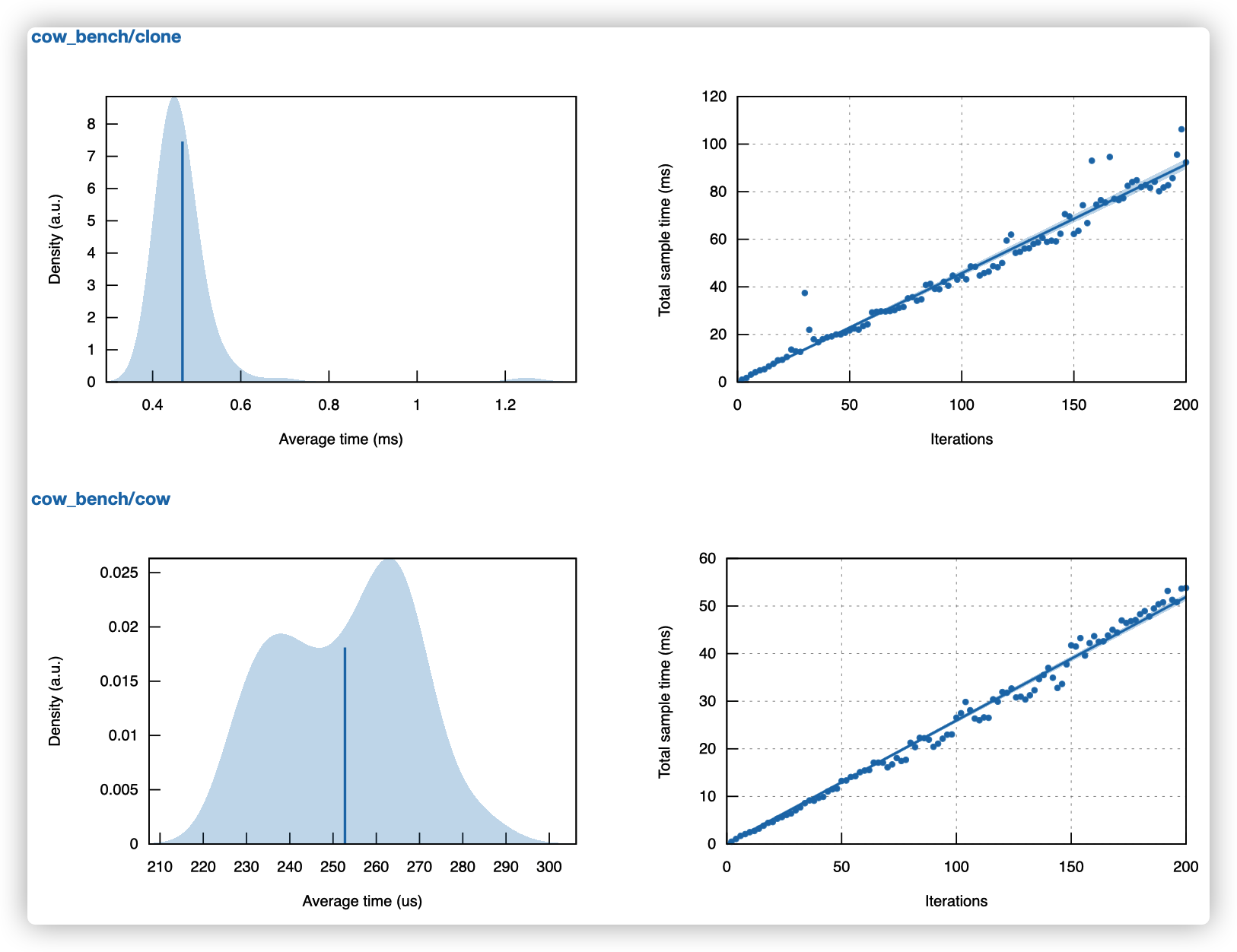
cow_bench/cow time: [256.10 us 259.48 us 262.41 us]
cow_bench/clone time: [448.13 us 457.38 us 467.73 us]
|
生成分析图片如下图所示,可见Cow在大量的内存操作时,能尽可能的进行内存共享,延迟耗时的克隆操作,进行更加细致的内存操作控制。
 OneStep
OneStep